What Exactly Causes Pain In The Heel

Overview
Do you have sharp, stabbing, and/or aching pain on the bottom of your heel or arch?
Is the pain more severe when you first get up in the morning or when you first start walking after rest? If this describes your pain then you probably suffer from a condition known as PLANTAR FASCIITIS. It sounds complicated, but plantar fasciitis is actually one of the most common foot problems. In the past plantar fasciitis has been called by other names, such as heel spur syndrome, bone spurs or a stone bruise on the heel. The plantar fascia is a long thick ligament that runs along the arch of your foot from your heel bone (the calcaneus) to the ball of the foot. The job of the plantar fascia is to help support your arch. When the fascia becomes inflamed and painful we call this PLANTAR FASCIITIS. The pain from plantar fasciitis most commonly occurs near the attachment of the fascia to the calcaneus (heel bone), which is why most people who suffer from plantar fasciitis have pain on the bottom or inside of the heel. However, the pain can be anywhere along the fascia from the heel to the ball of the foot.
Causes
There are several possible causes of plantar fasciitis, including wearing high heels, gaining weight, increased walking, standing, or stair-climbing. If you wear high-heeled shoes, including western-style boots, for long periods of time, the tough, tendonlike tissue of the bottom of your foot can become shorter. This layer of tissue is called fascia. Pain occurs when you stretch fascia that has shortened. This painful stretching might happen, for example, when you walk barefoot after getting out of bed in the morning. If you gain weight, you might be more likely to have plantar fasciitis, especially if you walk a lot or stand in shoes with poor heel cushioning. Normally there is a pad of fatty tissue under your heel bone. Weight gain might break down this fat pad and cause heel pain. Runners may get plantar fasciitis when they change their workout and increase their mileage or frequency of workouts. It can also occur with a change in exercise surface or terrain, or if your shoes are worn out and don't provide enough cushion for your heels. If the arches of your foot are abnormally high or low, you are more likely to develop plantar fasciitis than if your arches are normal.
Symptoms
The typical presentation is sharp pain localized at the anterior aspect of the calcaneus. Plantar fasciitis has a partial association with a heel spur (exostosis); however, many asymptomatic individuals have bony heel spurs, whereas many patients with plantar fasciitis do not have a spur.
Diagnosis
A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist is usually sufficient to diagnose plantar fasciitis. Occasionally, further investigations such as an X-ray, ultrasound or MRI may be required to assist with diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition.
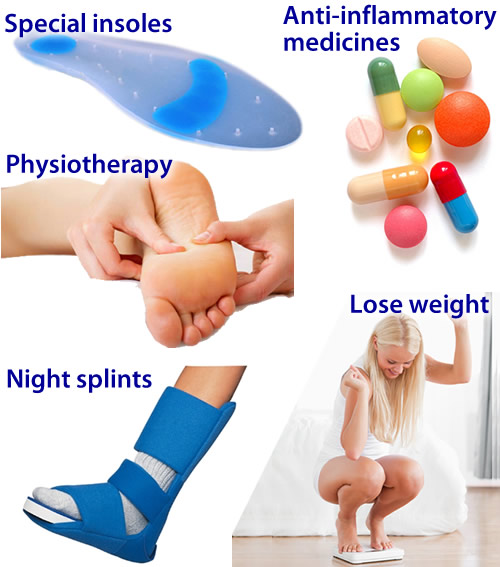
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment for plantar fasciitis includes medication, physical therapy, shock wave therapy, or surgery. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen are used to treat the inflammation and pain of plantar fasciitis, but they won’t cure the condition. Corticosteroids can also be used to ease pain and reduce inflammation. Corticosteroids are applied either as a topical solution in conjunction with a non-painful electric current or through injections to the affected area.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery for plantar fasciitis can be very successful in the right patients. While there are potential complications, about 70-80% of patients will find relief after plantar fascia release surgery. This may not be perfect, but if plantar fasciitis has been slowing you down for a year or more, it may well be worth these potential risks of surgery. New surgical techniques allow surgery to release the plantar fascia to be performed through small incisions using a tiny camera to locate and cut the plantar fascia. This procedure is called an endoscopic plantar fascia release. Some surgeons are concerned that the endoscopic plantar fascia release procedure increases the risk of damage to the small nerves of the foot. While there is no definitive answer that this endoscopic plantar fascia release is better or worse than a traditional plantar fascia release, most surgeons still prefer the traditional approach.
Stretching Exercises
Stretching your plantar fasciitis is something you can do at home to relieve pain and speed healing. Ice massage performed three to four times per day in 15 to 20 minute intervals is also something you can do to reduce inflammation and pain. Placing arch supports in your shoes absorbs shock and takes pressure off the plantar fascia.